Health Talk Blog
U.S. California
CASES DEATHS CASES DEATHS
December 2020 19,111,443 341,149 2,120,610 24,241
2021 Timeline
January 26,185,362 441,319 3,310,949 40,702
December 54,859,966 825,816 5,515,250 76,520
2022 Timeline
January 74,333,528 884,265 8,292,735 79,801
December 100,751,994 1,092,674 11,829,499 98,637
2023 Timeline
January 104,196,861 1,132,935 11,964,001 99,944
December 110,109,948 1,190,171 12,543,800 106,183
2024 Timeline
January 110,653,481 1,193,026 12,571,376 106,559
February 111,426,318 1,199,436 12,677,885 107,643
March 111 765 841 1,218,840 12,709,918 112,443
April 111,820,082 1,219,487 12,711,918 112,443
U.S. POPULATION - is 341,818,907 of 30 June 2024, 8:23 p.m. PST based on Census U.S. and World Population Clock.
UPDATED WEEKLY – Worldometer, Last updated on 30 June 2024
- Total Cases - 704,753,890
- Total Deaths - 7,010,681
- Recovered* - 675,619,811
* updated information
** no updated information at this reporting
NOTE: As of April 13, 2024, the Coronavirus Tracker is no longer being updated due to the unfeasibility of providing statistically valid global totals, as the majority of countries have now stopped reporting. However, historical data remain accessible. Worldometer delivered the most accurate and timely global statistics to users and institutions around the world at a time when this was extremely challenging. We thank everyone who participated in this extraordinary collaborative effort.
- Employment increased by 272,000 in May
- Unemployment rose slightly to 4%
JUNE – JULY BLOG
HEALTH UPDATES
Returning - First case of rare, sexually transmitted form of ringworm reported in the U.S. Updated Sun, June 9, 2024 at 5:28 AM PDT. A sexually transmitted ringworm caused by a rare fungus, has been reported in the United States. Tests revealed a sexually transmitted fungus first time identified in the U.S, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, type VII. 2023, doctors in France reported 13 such cases, twelve were men who had sex with men.
The case was first reported in JAMA Dermatology by doctors at NYU Langone Health, New York City. A man, in his 30s from New York City, reported having sex with multiple men during a trip to England, Greece and California. Returning home, he developed a red, itchy rash on his legs, across his groin and buttocks.
His infection took four and a half months to fully heal but responded to standard anti-fungal medications. Treatment initially included oral anti-fungals - fluconazole for four weeks, six weeks of terbinafine, then approximately eight additional weeks of itraconazole.
Rash may look like eczema. The rash may look like an eczema flare up than the typical ringworm infections, that form in circles. The infection is not life-threatening but can cause permanent scarring. Trichophyton indotineae, is not considered an STI’s, but is drug-resistant and highly contagious. Trichophyton mentagrophytes, type VII, is treatable.
The NYU Langone Health team has identified a total of 11 cases of Trichophyton indotineae ringworm in both men and women in New York City. Jeremy Gold, medical epidemiologist, Center for Disease Control and Prevention stressed, “doctors should consider fungi along with viruses and bacteria as a potential cause of sexually transmitted disease.
Tuberculosis outbreak declared public health emergency in Long Beach, but overall risk remains low, officials say. Fri, May 3, 2024 at 1:25 PM PD. A public health emergency was declared by City Health Officer, Dr. Anissa Davis, Long Beach, California in response to an outbreak of tuberculosis according to a city announcement.
The city health department’s investigation identified approximately 170 people who have probably been exposed to tuberculosis. The overall, “risk of TB for people who live, work, study or visit Long Beach remains very low.”
Tuberculosis, TB, is a bacterial infection, usually in the lungs, that can cause coughing, chest pain and fever – but characterized by coughing up blood or mucus. TB was found among several people associated with a single room occupancy hotel in Long Beach. 14 cases were associated with the outbreak, nine hospitalized at some point in their illness and one person has died. The city indicated “people staying at the hotel or who may otherwise have been exposed, will be contacted by the health department.
“The outbreak is currently isolated to a distinct population, with a low risk to the general public. The population at risk, has significant barriers to care:
- homelessness,
- housing insecurity,
- mental illness,
- substance use and
- serious medical comorbidities.
Screening and treating large numbers requires many resources. Declaring a public health emergency streamlines the ability to quickly secure resources and take additional action to contain the outbreak.”
Tuberculosis is curable, often treated with a standardized course of drugs that usually includes antibacterial medicines. It can also be prevented with screenings, vaccinations and assuring people infected, finish their course of treatment.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported tuberculosis cases last year, across the United States, appeared to be returning to levels seen before the Covid-19 pandemic.
Cases increased slightly in 2022 after a 20.2% decline in 2020 and a 9.8% increase in 2021, according to the data published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
170 people 'likely exposed' to tuberculosis in Long Beach outbreak. Health officials have warned of an ongoing tuberculosis outbreak in Long Beach, California. The city's health officer, Dr. Anissa Davis, made the declaration, with the Long Beach City Council considering formal approval.
The outbreak follows an uptick in TB across the entire state of California. 2,100 active cases were reported last year, 15% more than were reported in 2022, marking a return to levels of active TB seen prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Tuberculosis, caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis microbe, can lie latent in the body, initially without symptoms, then activates if the immune system is weakened by age or disease. About 5% to 10% of people who carry the bacteria ultimately develop active TB.
VARIANT UPDATES
COVID variant LB.1 is rising across the US: Here's what you need to know about it. USA TODAY. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC, is tracking the growth of the COVID-19 LB.1 variant as it begins to trail KP.3.
For two-weeks in June, the CDC’s Nowcast data tracker showed projections of the COVID-19 variants. KP.3 accounted for 33.1% of positive infections, followed by KP.2 at 20.8%. The new variant, LB.1, was at 17.5% and JN.1, the previous ring-leader, at 1.6% of positive cases.
CDC Spokesperson, Dave Daigle, said “the LB.1 variant has the potential to infect some people more easily based on a single deletion in a spike protein.” This spike of the LB.1 variant is like the ones seen in JN.1 lineages which saw a single change in spike, unlike KP.3 variant, a sub lineage of JN.1, which had two changes in spike. One of the two changes in spike was observed in earlier lineages, XBB.1.5, dominant throughout 2023 and the basis for the 2023–2024 vaccine formulation.
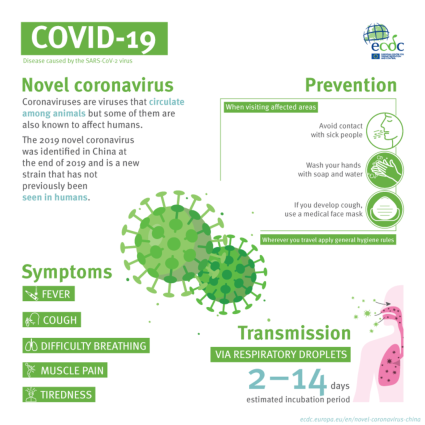
Symptoms of COVID-19. The CDC has not said if LB.1 has its own specific symptoms. However, the government agency outlines the basic symptoms of COVID-19 on its website. Symptoms can appear between two to 14 days after exposure to the virus and can range from mild to severe.
U.S. Preparedness and Response to Increasing Clade I Mpox Cases in the Democratic Republic of the Congo — United States, 2024. Weekly / May 16, 2024 / 73(19);435–440.
Summary
- What is already known about this topic? - Compared with clade II monkeypox virus, MPXV, which caused the 2022 global mpox outbreak, clade I MPXV can result in more persons with severe illness and higher mortality.
- What is added by this report? - The increasing number of reported clade I mpox cases in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, DRC, poses a global threat for potential spread. No clade I cases have been reported in countries without endemic transmission, persisting in a population or region, generally having settled to a relatively constant rate of occurrence.
- What are the implications for public health practice? - U.S. clinicians and public health practitioners should be alert for cases in travelers from DRC and request clade-specific testing. Appropriate medical treatment is critical given the potential for severe illness, contact tracing, containment strategies – including: isolation, behavior modification and vaccination.
Abstract
Clade I monkeypox virus, MPXV, can cause severe illness in more people than clade II MPXVs. The Democratic Republic of the Congo, DRC, has experienced an increase in suspected cases during 2023–2024. The increase in clade I cases raises concerns that the virus could spread to other countries and underscores the importance of coordinated, urgent global action to support DRC’s efforts to contain the virus.
To date, no cases of clade I mpox have been detected outside of countries in Central Africa. The CDC is enhancing U.S. preparedness by raising awareness, strengthening surveillance, expanding diagnostic testing capacity for clade I MPXV.
Introduction
MPXV can spread to people from contact with infected wildlife, or close, prolonged contact with persons infected with MPXV. The global clade II MPXV spread primarily via sexual contact among gay, bisexual or other men who have sex with men, MSM.
DRC Investigation and Findings. Epidemiology of Clade I MPXV in DRC. Data from DRC’s national infectious disease surveillance system was analyzed for this report, reviewed by the CDC, deemed not research.
Jan 1, 2023 – Apr 14, 2024, 19,919 cases of suspected clade I mpox§ and 975 deaths were reported from 25 of 26 provinces and the capital city, Kinshasa.
- Clade I mpox MPXV cases were reported among MSM and male and female sex workers and their contacts.
- 67% of suspected cases, 78% of deaths occurred in persons less than 15 years;
- children 12–59 months accounted for 28%
Demographic characteristics differed among provinces:
- Some provinces, Equateur, occurring primarily in persons ≤15 years or 69%
- Other provinces, South Kivu and Kinshasa, persons >15 years accounted for the largest proportion of cases or 69%.
- During January 1, 2023 – April 14, 2024, 50% of DRC’s suspected mpox cases were reported from Equateur province. Equateur province reported elevated CFR, 5.7%, compared with CFRs reported elsewhere in the country, 4.3%.
- In remote locations, many suspected cases are not tested for MPXV, with testing varying widely by province.
CDC Support to DRC. The CDC’s support for DRC’s mpox-related activities during the last 15 years has included establishing laboratory testing and training, supporting diagnostic testing and genetic sequencing, conducting JYNNEOS vaccine clinical research. In response to the current outbreak, the U.S. government established an interagency response team to coordinate support to DRC and neighboring countries to direct U.S. preparedness efforts. The U.S. government is providing funding, technical assistance, and personnel deployments to support the DRC response.
U.S. Public Health Preparedness and Response. Notifications and At-Risk U.S. Populations. The CDC issued a Health Alert Network notice on December 7, 2023, urging U.S. clinicians to consider clade I MPXV infection in persons with mpox signs and symptoms, recently in the DRC, recommending expedited clade-specific testing.
The CDC also issued a Level 2 Travel Health Notice for the DRC, although to date, no cases of clade I mpox have been reported in the United States or in any countries where the virus is not endemic. Documented sexual transmission of clade I MPXV in DRC – MSM, multiple sexual partners, sex workers, may be at increased risk if clade I mpox is introduced into the United States.
Clade I MPXV transmission is more commonly reported among children. Transmission among children in the United States is considered much less likely because of:
- absence of zoonotic reservoirs – disease of animals, such as rabies or psittacosis, that can be transmitted to humans.
- fewer household occupants, and
- widely available cleaning and hygiene resources.
Current CDC Activities and Recommendations. Recommendations include:
- Aiding early containment measures, including contact tracing, isolating patients,
- Offering JYNNEOS vaccine to contacts, and
- Strictly adhering to recommended infection prevention and control practices in health care settings.
- In the United States, only 23% of persons at risk for clade II MPXV infection have completed the 2-dose JYNNEOS vaccination series.
MPXV Testing. The U.S. mpox diagnostic testing strategy includes the CDC’s Food and Drug Administration, FDA, cleared nonvariola orthopoxvirus, NVO, PCR test. A positive test result provides a presumptive diagnosis of mpox; however, the test cannot distinguish between clades.
The CDC recommends the NVO test be used in addition to clade-specific testing, and positive or negative clade II test results be further investigated through sequence analysis.
Discussion. The 2014 West Africa Ebolavirus outbreak demonstrated risks associated with a delayed global response to a serious pandemic threat. The United States launched a robust domestic response to the 2022 clade II MPXV outbreak, based on 2 decades of smallpox preparedness.
However, the global public health community missed earlier opportunities to recognize the threat and help contain clade II mpox, spreading person-to-person in Nigeria as early as 2016. The recent increases in clade I MPXV transmission in DRC pose a new risk for global spread if the virus is not urgently contained.
What to Know About COVID FLiRT Variants. Virologists are keeping an eye on several COVID variants that have all picked up the same set of mutations. Here’s what that means. May 13, 2024. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. According to the CDC, by the end of March, the KP.2 variant was causing 4% of infections in the U.S., while its parental strain, JN.1, was causing over 50% of infections. Early May, KP.2 made up 28% f infections, overtaking JN.1 as the dominant variant. KP.2, one of several variants referred to as “FLiRT “ variant, named after the technical names for their mutations.
What are these “FLiRT variants”? The term is used to describe a family of different variants, including KP.2, JN.1.7 and any other variants starting with KP or JN, that have independently picked up the same set of mutations or convergent evolution. All are descendants of the JN.1 variant, dominant in the U.S. for the past several months. The “FLiRT”s or “FLip”s mutations refer to specific positions in the spike protein, this case, positions 456, 346, and 572.
Viruses like SARS-CoV-2 mutate frequently. to evade recognition by antibodies, often weakening their ability to bind to the cells they want to infect. Mutations develop that improve binding ability. Different variants picking up the same mutations tells virologists that this combination of mutations is helping the virus accomplish the goal.
How do these mutations help the virus bind to cells while evading antibodies? Two mutations, 456 and 346, eliminate binding sites for antibodies that neutralize SARS-CoV-2. However, those same antibody binding sites are important for the virus to bind to and enter cells. By evading antibodies, the FLiRT variants may also lose some ability to bind to their receptor. The 572 mutation allows the virus to more tightly bind to cells, ultimately causing infection.
Do people who recently had COVID have any protection against infection from FLiRT variants?
A JN.1 infection should provide strong protection against all the FLiRT variants. There are still a other places antibodies can bind to. Infection from a variant older than JN.1 is less likely to offer as much protection.
Do we know yet how well the current COVID-19 vaccines work against the FLiRT variants? Against JN.1, the vaccine designed around XBB.1.5, does generate some cross-reactive antibodies. Studies have not been yet done with some of these newer variants, but those are likely to be a little less cross-reactive.
Should we anticipate these variants to drive a surge in cases this summer? It’s certainly possible! While the waves are becoming smaller, they are still having the greatest impact on our susceptible populations: the elderly, immunocompromised and those with other secondary medical conditions.
How might these variants impact plans for the COVID vaccine formula that gets updated for the fall? This is the time of year when governing bodies like the WHO and FDA recommend a formulation for updated COVID vaccines that will roll out in early fall. Last year, the vaccines were based on the XBB.1.5 variant, a few months later, the JN.1 variant became the dominant variant in the U.S.
The WHO announced their COVID vaccine advisory group recommended using the JN.1 lineage as the antigen for the upcoming formulations. All FLiRT variants are within the JN.1 family of variants. In the U.S., the FDA postponed its meeting to determine the fall 2024 COVID vaccine to early June, giving them time to see which of the FLiRT variants is becoming dominant to fine-tune the WHO recommendation.
What are the usual symptoms and transmission timeline for FLiRT variants? When it comes to symptoms, we’re not seeing anything new or different with these variants. We continue to see more mild disease, but that’s likely not because the virus is milder, but because our immunity is much stronger. After vaccinations and infections, most of the population is better able to fight off an infection without much concern for severe disease. The period of infectiousness for the FLiRT variants remains the same as JN.1 and previous omicron variants after exposure:
- May take five or more days before developing symptoms, though symptoms may appear sooner.
- You are contagious one to two days before you experience symptoms and a few days after symptoms subside.
- As with previous variants, some may have detectable live virus up to a week after their symptoms begin, and
- Some may experience rebound symptoms.
- At-home testing remains a really important tool for knowing whether you could potentially infect others.
Are antivirals like Paxlovid effective against FLiRT variants? Yes! Paxlovid works against variants up to JN.1 and is still recommended for high risk individuals. Based on the sequencing of the FLiRT variants, they should still be susceptible to Paxlovid, as well as antiviral drugs, molnupiravir and remdesivir.
How can people protect themselves and their loved ones as we head into summer? Keep an eye on case rates in your region or anywhere you plan to travel when deciding whether you should take additional precautions, like wearing a mask or gathering in well-ventilated areas. Some local health departments report on virus levels in wastewater, which can signal an upcoming rise in cases.
It’s always a good idea to keep a few COVID tests. in case you start to feel sick. Testing, at home or in a health care setting, to assure you know what you're infected with.
2 new COVID variants called 'FLiRT' are spreading in the U.S. What are the symptoms? Fri, May 3, 2024 at 3:38 PM PDT. Respiratory virus season may be ending in the United States, but a new group of COVID-19 variants are circulating, nicknamed "FLiRT." KP.2 quickly overtook JN.1, the omicron subvariant that drove a COVID surge this past winter. Currently, KP.2 accounts for 1 in 4 infections nationwide, according to data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- KP.2 made up nearly 25% of cases in the U.S. in a 2 week period in April, up from 10% during the previous two-week period ending April 13.
- JN.1, the next most common variant, is accounting for 22% of cases, followed by two JN.1 subvariants, JN.1.7 and JN.1.13.1.
- Another FLiRT variant, KP.1.1, is also circulating in the U.S., but less widespread than KP.2, accounting for 7.5% of infections nationwide, per the CDC.
What are the FLIRT variants? FLiRT variants, KP.2 and KP.1.1, spinoffs of JN.1.11.1, a direct descendant of JN.1, were initially detected in wastewater samples across the country. The new variants have two additional mutations that set them apart from JN.1 and appear to give them an advantage over previous variants, Dr. Albert Ko, infectious disease physician and professor of public health, epidemiology and medicine at Yale School of Public Health.
According to the Infectious Disease Society of America, the nickname 'FLiRT’ is based on the technical names for their mutations. Like other COVID-19 strains, JN.1, HV.1, EG.5 aka Eris, XBB.1.16 or Arcturus, FLiRT variants are part of the omicron family.
Are the new variants more transmissible? “It’s still early days, but the initial impression is this variant, KP.2, is rather transmissible,” Dr. William Schaffner, professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University Medical Center.
Over 97% of people in the U.S. have natural or vaccine-induced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 virus, per the CDC, but this immune protection fades over time. Low vaccination rates and waning immunity create a vulnerable population, which may allow the FLiRT variants to take hold.
Symptoms of the FLiRT variants are similar to those caused by JN.1, which include:
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Fatigue
- Congestion
- Runny nose
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Fever or chills
- New loss of sense of taste or smell
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
FLiRT – All You Need To Know About The Latest COVID-19 Variants. Look at you, over there, batting your spike proteins at me! There’s a family of new COVID-19 variants nicknamed the FLiRT variants. Here’s what we know about them so far. These latest variants are derivatives of JN.1, according to physician-scientist, Eric Topol, Scripps Research Institute explained in his newsletter, Ground Truths, the new variants have picked up mutations in their spike proteins.
- In one location, an amino acid labeled “F” was switched for one labeled “L”
- In another, an “R” was swapped for a “T”.
- Put those letters together, with the addition of an “I”, you get FLiRT.
The KP.2 variant, seems to be leading and suggests it could now be responsible for almost a quarter of infections. KP.2 was able to spread more easily than JN.1 and may also be more resistant to immune responses from vaccines and prior infections. The World Health Organization released a statement recommending future COVID-19 vaccine formulations specifically target JN.1 and its derivatives.
VACCINE UPDATE
COVID-19 Vaccines for Use in the United States Beginning in Fall 2024. FDA Updates Advice to Manufacturers of COVID-19 Vaccines (2024-2025 Formula): If Feasible Use KP.2 Strain of JN.1-Lineage. FDA's Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee, VRBPAC, met June 5, 2024, to discuss and make recommendations on the COVID-19 vaccine selection of the 2024-2025 Formula for use in the United States beginning the fall of 2024. The committee unanimously voted to recommend a monovalent JN.1-lineage vaccine composition.
The FDA continues to monitor the circulating strains of SARS-CoV-2. Based on current available data, recent rise in cases of COVID-19 in areas of the country, the agency determined the preferred JN.1-lineage for 2024-2025 Formula COVID-19 vaccines is the KP.2 strain. The change is intended to ensure that the 2024-2025 Formula COVID-19 vaccines more closely match circulating SARS-CoV-2 strains.
The Updated COVID Vaccines Are Here: 9 Things to Know. Family Health. APRIL 19, 2024. There has been better protection against severe disease, hospitalization and death from the 2023–2024 Formula mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. Shots are available to protect everyone 6 months and older from serious illness, hospitalization and death from the disease.
The Food and Drug Administration, FDA, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC, approved updated vaccines by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna for everyone 6 months and older, and authorized an updated Novavax vaccine for those 12 and older in 2023. In February 2024, the CDC recommended an additional dose for adults ages 65 and older.
The vaccines target XBB.1.5, subvariant of Omicron, but the CDC indicated updated vaccines should also work against currently circulating variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The vaccine is expected to protect against JN.1, the current dominant strain in the U.S.
COVID and flu vaccine—here's how it could benefit public health. Medical Xpress. Earlier this week, Moderna announced positive results for its phase 3 clinical trial of a combined vaccine against COVID and influenza. So what exactly did the trial find?
Combination vaccines are already used for other diseases. Combination vaccines have successfully been used for decades in Australia and around the world.
- The DTP vaccine, combines protection against diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis or whooping cough, was first administered in 1948.
- A hexavalent vaccine, protects against six diseases—diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, hepatitis B and Haemophilus influenzae type b, an infection that can cause brain swelling, is part of routine childhood immunization programs in Australia and elsewhere.
- MMR vaccine, given to children to protect against measles, mumps and rubella.
Moderna's phase 3 trial, 8,000 participants, half aged 50 to 64, the other half aged 65 and up. From a safety perspective, the combined vaccine reactions were similar across the experimental and control groups, with the most common side effects: muscle aches, fatigue and pain at the injection site.
- The age 50-to-64 control group, were given the Fluarix flu vaccine, and Moderna's mRNA COVID vaccine, Spikevax.
- The over-65 control group received Spikevax alongside Fluzone HD, an enhanced flu vaccine, designed specifically for older adults.
Moderna reported the combined vaccine elicited a higher immune response in both age groups against COVID and three influenza strains.
How to Protect Yourself? Getting vaccinated is your best bet!
IT’S NOT OVER!
Stay safe. Mask. Social distance. Frequent hand washing. Avoid crowds
ALWAYS CONSULT YOUR PERSONAL HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONAL
- https://www.yahoo.com/news/tuberculosis-outbreak-declared-public-health-202531022.html
- https://www.livescience.com/health/viruses-infections-disease/170-people-likely-exposed-to-tuberculosis-in-long-beach-outbreak
- https://www.iflscience.com/flirt-all-you-need-to-know-about-the-latest-covid-19-variants-74007
- https://publichealth.jhu.edu/2024/what-to-know-about-covid-flirt-variants
- https://www.yahoo.com/news/first-case-rare-sexually-transmitted-195135075.html
- https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/updated-covid-19-vaccines-use-united-states-beginning-fall-2024
- https://www.msn.com/en-us/health/other/results-are-looking-promising-for-a-combined-covid-and-flu-vaccine-heres-how-it-could-benefit-public-health/ar-BB1ohAIp?ocid=BingNewsSearch
- https://www.yalemedicine.org/news/updated-covid-vaccine-10-things-to-know
- https://www.msn.com/en-us/health/other/covid-variant-lb1-is-rising-across-the-us-heres-what-you-need-to-know-about-it/ar-BB1p16ho?ocid=BingNewsSerp
Comments
-
Great blog! I left my position in brilliant hands! Very Informational!
-
I found your COPD comments interesting. Would you consider doing a leaky gut syndrome segment?